Ketamine usually starts working in 40 minutes to 2 hours. Many patients feel anxiety relief within the first hour. The speed varies by how you administer ketamine. IV infusions work the fastest. Next are intramuscular injections, then nasal spray, and finally sublingual forms.
Knowing how fast ketamine works for anxiety helps patients set realistic expectations. It also helps them make informed choices about this new treatment option. Ketamine works quickly, unlike traditional anxiety medications that take weeks to help. This fast effect gives hope to those with severe, treatment-resistant anxiety.
Medical Disclaimer:
This article is for educational purposes only. It is not medical advice. Ketamine therapy for anxiety represents an off-label use requiring qualified medical supervision. Always consult healthcare professionals before considering ketamine treatment. This information shows the latest clinical knowledge and research published by November 2024.
Editorial Standards:
Content comes from peer-reviewed research, clinical guidelines by the American Psychiatric Association, and FDA-approved medication details.
No conflicts of interest to declare.
What Is Ketamine and How Does It Work?
Medical Background and Mechanism of Action
Researchers created ketamine in 1962 as an anesthetic. It got FDA approval in 1970 for use in surgery. The FDA drug database shows that this medication acts as an NMDA receptor antagonist. It blocks receptors that usually respond to glutamate, the brain's main excitatory neurotransmitter.
Research in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry shows how ketamine helps with anxiety. It works by increasing glutamate release. This activates AMPA receptors, which promote the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Researchers at major centers found that this protein helps neurons grow and connect. This process leads to synaptogenesis, which is the formation of new neural connections. Neuroplastic changes can help reverse the brain shrinkage from chronic stress and anxiety disorders.
Ketamine works differently from traditional anxiety medications. While those target serotonin or GABA systems, ketamine focuses on glutamate. This makes its approach unique. The National Institute of Mental Health explains why ketamine works faster than regular antidepressants. It also helps some people who don’t respond to regular treatments.
Role in Mood and Anxiety Relief
Ketamine influences mood and anxiety through many pathways beyond NMDA receptor blockade. Yale School of Medicine research shows that the medication targets opioid receptors. This may help explain its quick mood-lifting effects. Neuroimaging studies show it affects the brain's default mode network. This system is active when we rest or reflect. People with anxiety disorders often have hyperactivity in this area.
Psychiatrists specializing in ketamine therapy believe the dissociative experience can help patients. This feeling gives them distance from anxiety symptoms. It also allows for new perspectives and better emotional processing. Understanding psychiatric disorders helps explain how ketamine targets the brain's role in anxiety.
Ketamine for Anxiety: An Overview
Why Ketamine Is Used for Anxiety Treatment
Doctors first used ketamine for anxiety after seeing how fast it lifted the mood in depressed patients. Many of these patients also felt much less anxious. Traditional anxiety treatments have big limits. This makes ketamine a good option for some patients.
SSRIs and SNRIs take 4-8 weeks to work. This means patients may struggle while they wait. Benzodiazepines work rapidly but carry addiction risks and cognitive side effects. Many people don’t respond well to current treatments. This creates a strong need for alternatives. Treatment-resistant anxiety impacts many patients. They often try several medications and therapy methods but find little relief.
Ketamine infusion therapy for anxiety offers hope when other options have failed. Quick response time helps those in acute crises or severe anxiety. It aids people whose symptoms disrupt daily life and relationships.
Treatment Administration Methods
Intravenous (IV) ketamine infusions
IV ketamine for anxiety represents the most studied administration method:
-
Involves a slow infusion over 40 minutes to several hours.
-
Occurs in medical settings with continuous monitoring.
-
Produces noticeable effects during the infusion period.
-
Allows precise dose control and immediate intervention if needed.
-
Full anti-anxiety benefits emerge over the following hours and days.
Intramuscular (IM) injections
A healthcare provider injects ketamine IM for anxiety into the muscle tissue. Effects start in 15 to 30 minutes. This method is quicker than oral forms but slower than IV administration. It requires less equipment and still has a fast onset.
Sublingual Tablets and Lozenges
Ketamine lozenges for anxiety dissolve under the tongue. They usually take 15 to 45 minutes to work. This method is easy to use at home with medical oversight. However, absorption rates differ more than with injections.
Esketamine nasal spray
Ketamine nasal spray for anxiety (Spravato) demonstrates effectiveness within 20-40 minutes. The FDA approves it for treatment-resistant depression. It can also help with anxiety symptoms that come with depression. However, it needs special administration protocols and monitoring.
Effectiveness Across Anxiety Conditions
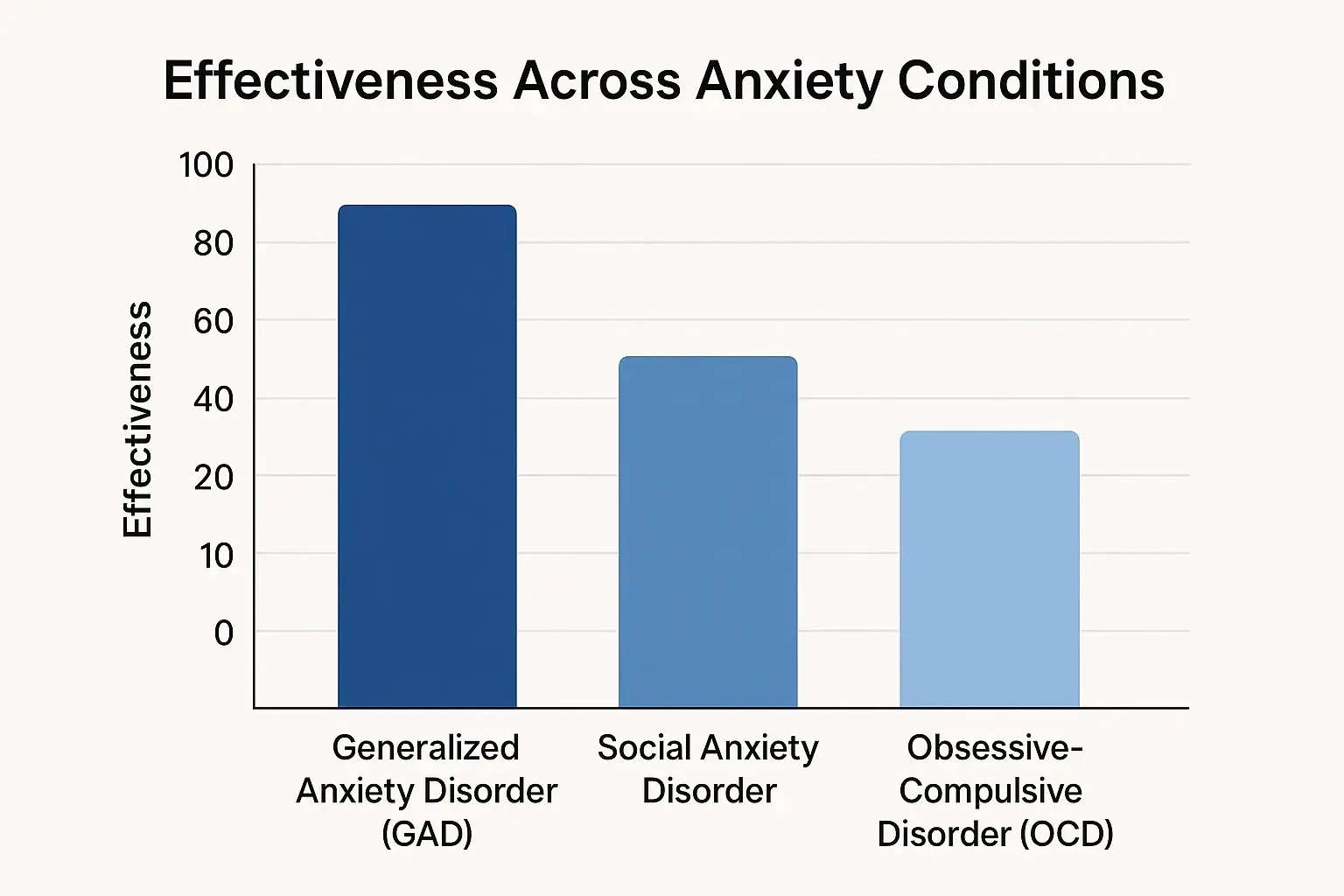 Ketamine shows promise for anxiety disorders. Research highlights its effectiveness across different conditions.
Ketamine shows promise for anxiety disorders. Research highlights its effectiveness across different conditions.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
A 2020 study in the Journal of Psychopharmacology examined ketamine for generalized anxiety. Sixty-seven percent of participants showed a big drop in anxiety after treatment. Clinical trial data show that many participants feel less worried.
They manage anxious thoughts better and feel less physical tension just hours after taking ketamine. Psychiatrists treating GAD patients see that ketamine offers quick relief. This is a stark contrast to traditional treatments, which can take weeks or months to work fully.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Research from anxiety disorder treatment centers shows that ketamine might help with social anxiety. It seems to reduce the intense self-focused attention seen in social anxiety. Patients often say they feel less burdened by social anxiety thoughts. They also report reduced worry about future social situations. Treatment specialists see lasting improvements in social comfort. These changes can last from days to weeks after treatment.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Clinical evidence for ketamine treatment for OCD and anxiety is mixed. Some studies show strong symptom reduction, but others report only modest benefits. Yale OCD researchers say OCD affects different brain circuits than other anxiety disorders.
This could explain why ketamine works differently for each condition. Experts say people with OCD and high anxiety might feel better with anxiety treatments. This can help them, even if their obsessions don’t get much better.
How Fast Does Ketamine Work for Anxiety?
Typical Onset Time by Administration Method
How quickly ketamine works for anxiety depends a lot on how it is delivered. This is based on clinical treatment protocols used at specialized ketamine clinics.
IV Infusion Timeline
Clinical observations from treatment centers show initial effects typically appear within 40 minutes. Many patients notice subtle changes during the infusion. They may feel lighter or have shifts in perception.
Healthcare providers often see dissociative effects start first. Then, they notice improvements in mood and anxiety over the next few hours. Research data indicate peak therapeutic effects typically occur 24 to 72 hours post-treatment.
Intramuscular Injection Timeline
Patients typically feel effects within 15 to 30 minutes after an IM injection, say medical practitioners. Peak effects occur 30 to 60 minutes post-administration based on clinical monitoring. Patients often say that anxiety relief starts slowly after the injection. The best results usually show up in the first few hours.
Sublingual and Nasal Spray Timeline
FDA-approved esketamine (Spravato) starts to take effect 20-40 minutes after you take it. Full anxiety relief develops within 1-2 hours in most cases. Absorption can vary with these methods. Some people respond faster or slower than average. This means we need to watch each individual closely.
Factors Influencing Response Speed
Ketamine's speed of action varies by person. This difference comes from several factors noted in clinical studies. Dose size greatly impacts how quickly effects start. Higher doses often lead to quicker, stronger results. Treatment protocols from psychiatric journals note this. Treatment specialists aim for quick relief but must consider side effects and safety risks.
Individual metabolism is key. Age, liver function, body makeup, and genetics all affect how people respond to ketamine. This leads to variations in the timing and duration of effects. Pharmacological studies show that these metabolic differences can change how drugs work. This can vary by 30-50% between individuals.
Anxiety severity influences perceived response time based on clinical observations. Psychiatrists notice that people with severe anxiety often feel relief faster than those with milder symptoms. The difference between their states before and after treatment is more noticeable. Severe anxiety may need several sessions for noticeable improvement based on treatment data.
Treatment history also affects response patterns documented in medical literature. Past medication trials don't always show how someone will respond to ketamine. This gives hope to those who haven’t found relief with standard treatments. Clinical experience shows that past therapy affects expectations. It also influences how quickly people notice symptom improvements.
Duration of Effects
The effects of ketamine for anxiety usually last about 7 to 14 days after a single treatment. However, this can differ significantly among individuals. Some people feel effects that last a few days. Others enjoy benefits for more than a month.
The duration depends on whether ketamine addresses neurobiological factors or just eases symptoms.
Factors that affect how long benefits last include:
-
Treatment frequency and consistency.
-
Combination with therapy or other treatments.
-
Lifestyle factors like sleep quality and stress management.
-
Severity and chronicity of the anxiety disorder.
Treatment Protocols and Maintenance
Initial Treatment Series
How many ketamine treatments for anxiety someone needs varies considerably between individuals. The typical initial series involves 4-6 infusions administered over 2-3 weeks. After the initial series, healthcare providers check how patients respond. They work with patients to decide if maintenance treatments are useful. They also determine how often these treatments should occur.
Maintenance Schedules
How often you need ketamine infusions for anxiety depends on your response. Some people get monthly infusions for lasting relief. Others need treatments every 2-3 weeks if their symptoms come back quickly. People with longer-lasting effects might need sessions every few months. Others may choose treatments only during stressful times.
The goal is to find the lowest treatment frequency that manages anxiety. This should also cut down on time and medical involvement. Learning how to calm anxiety naturally can boost the benefits of ketamine. These strategies work well between sessions.
Potential Side Effects and Safety
Common Short-Term Side Effects
Ketamine can cause side effects when used for anxiety treatment. Common effects include dissociation and changes in perception. This information comes from clinical safety data.
During Treatment
Patients often report feeling detached from their surroundings. They may notice distorted time perception. Some experience changes in vision or hearing. Others sense floating or out-of-body feelings. Mental health professionals prepare patients for these experiences through pre-treatment education.
After Treatment
Clinical monitoring data show that dizziness and coordination problems often occur. Nausea occurs in about 30% of patients, according to treatment center statistics. Vital sign monitoring shows short-term rises in blood pressure and heart rate during treatment. Post-treatment assessments document temporary confusion, headaches, and fatigue in some patients.
Most side effects fade within 1-2 hours after the IV infusion ends, according to clinical protocols. Ketamine treatment teams offer support during episodes and closely monitor recovery.
Safety Considerations
Is ketamine safe for anxiety long-term? It requires ongoing monitoring according to medical guidelines. Current studies show that medical supervision ensures safety over multiple years. Long-term data are still limited compared to traditional meds from the 1980s and 1990s.
The American Psychiatric Association highlights some concerns with frequent use. High-dose users may face bladder issues. Daily recreational use at much higher doses can lead to cognitive effects. The addiction potential seems low in medical settings. Research in addiction medicine shows that controlled dosing and monitoring can really reduce the risk of abuse.
Required Medical Supervision
Ketamine treatment for anxiety requires qualified oversight.
Before Treatment
-
Comprehensive psychiatric assessment
-
Medical history and physical examination
-
Cardiovascular screening
-
Discussion of expectations and risks.
During Sessions
-
Continuous observation by trained staff.
-
Vital sign monitoring
-
Psychological support during dissociation.
-
Extended observation after completion.
Ongoing Care
-
Regular assessment of treatment response
-
Side effect monitoring
-
Coordination with other treatments.
-
Evaluation of continued appropriateness
Who Can Benefit from Ketamine
People who might consider ketamine for anxiety are those with treatment-resistant anxiety. This usually includes people who haven't responded well to at least two different medications and therapy. These individuals experience significant functional impairment from anxiety symptoms despite conventional treatment attempts.
People with severe anxiety and suicidal thoughts might find ketamine helpful. It works quickly and can help create a safe space. This can also lead to longer-term treatment plans. Ketamine can help people who have both anxiety and depression at the same time.
People who struggle with side effects from common medications, like sexual dysfunction or weight gain from SSRIs, might think about using ketamine. It can offer relief without these specific problems.
Groups Requiring Caution
Certain populations need special considerations when exploring ketamine treatment. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals have safety concerns. There is not much human data available, and the medication can pass into breast milk. Ketamine is usually avoided in pregnancy. This is unless the benefits clearly outweigh the unknown risks.
Adolescents and young adults need careful evaluation and supervision. Their developing brains can be more sensitive to dissociative drugs. Severe anxiety can also hinder healthy development. Risk-benefit analysis must be thorough and individualized for younger patients.
Older adults might react more to ketamine's side effects and heart changes. So, they may need dose adjustments and closer monitoring. Elderly patients with severe anxiety may enjoy treatment. But they require close medical supervision.
People with certain psychiatric conditions need caution. Active psychosis or schizophrenia is are red flag. They may worsen psychotic symptoms. People with substance use disorders need careful evaluation for relapse risk. Medical ketamine use is very different from using drugs recreationally.
The Future of Ketamine Treatment
Ongoing Research
Ketamine research for anxiety is growing. Many clinical trials are exploring:
-
Best dosing protocols
-
How it compares to standard treatments.
-
Reasons for individual response differences.
-
Long-term safety profiles
This research aims to improve understanding and treatment options.
Researchers are looking into new ketamine derivatives and ways to administer them. They want to keep the benefits but cut down on side effects.
Integration with Other Approaches
Ketamine and CBT for anxiety combination shows promise in early research. Ketamine may boost neuroplasticity. This can help create new thought patterns and behaviors. These changes are key in cognitive behavioral therapy. Some treatment protocols use ketamine for quick symptom relief. This fast anxiety reduction helps patients engage better in treatment. When symptoms are severe, therapy can feel overwhelming. So, ketamine supports both immediate and long-term therapy benefits.
The future may include personalized ketamine plans for anxiety. They will depend on personal traits, symptom patterns, and patient responses to treatment. Knowing five mental health issues helps us understand anxiety treatment better.
Conclusion
Clinical evidence and patient data show that the medication typically takes 40 minutes to 2 hours to work. Many patients feel significant anxiety relief by the first day of treatment. Ketamine’s quick response is its biggest benefit. Unlike traditional medications, which can take weeks to work, ketamine acts fast—treatment studies back this.
Ketamine treatment for anxiety gives hope to those with treatment-resistant symptoms. Many haven’t found relief from standard methods. Research from specialized centers supports this approach. Ketamine isn't the best choice for everyone. It's not the first option in treatment, according to current psychiatric guidelines. Selecting candidates carefully is crucial. This is due to the need for medical oversight, dissociative effects, and limited long-term data.
If you’re considering ketamine therapy for anxiety that hasn’t improved with other treatments, consult experts in this field. A thorough evaluation checks if ketamine is safe and suitable for managing anxiety. It also helps set realistic expectations for treatment.
Sources and References:
-
FDA Drug Safety Database
-
Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, various publications 2018–2024
-
National Institute of Mental Health research findings
-
American Psychiatric Association Treatment Guidelines
-
Yale School of Medicine ketamine research program
-
Clinical trial data from ClinicalTrials.gov






Comments